Discover tape's role in trimming the environmental impact of data storage in this whitepaper from Brad Johns Consulting
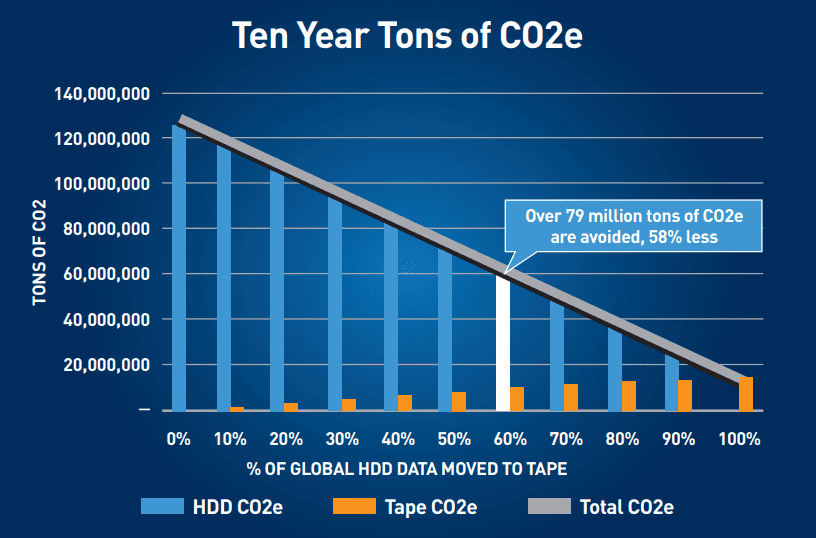
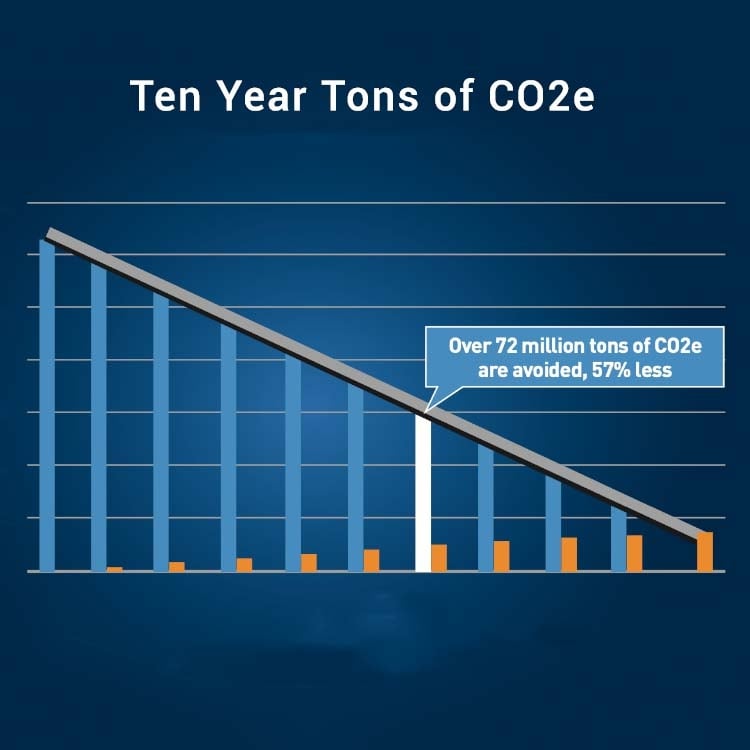
Learn MoreTape is an eco-friendly choice for data storage. Compared to use of other traditional technologies in data centers (such as hard disk drives), tape can drive a reduction in carbon emissions of as much as 97%. Fujifilm's dedication to sustainability starts with manufacturing eco-friendly forms of data storage. But it doesn't end there.
Use of Recycled Materials

Sustainable Forestry

Biodegradable Resources

01.
We work with responsible business partners and vendors who also seek to be environmentally friendly and reduce carbon footprints. For example, the pallet supplier we opt to work with strives to source wood and other materials responsibly and limit clear cutting to reduce the loss of forest cover.

02.
We use recycled and sustainable materials whenever possible. That includes using soy-based ink and seeking out suppliers that use recycled wastewater.


03.
Our Eco-Friendly data tape cartridge packaging eliminates up to 80% of packaging waste by weight compared to standard P-case product configuration that includes five pack corrugated inner cartons, individual cartridge p-cases and branded u-card.
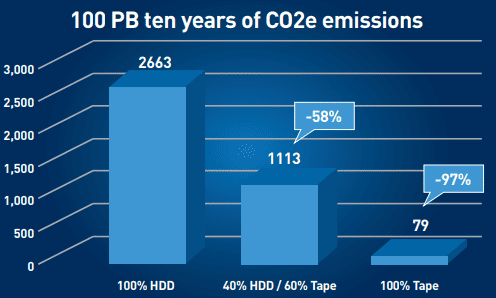
Tape systems consume about 87% less energy than equivalent amounts of hard disk storage and can produce up to a 97% reduction in CO2 emissions.
Disks are high energy consumers for a number of reasons. They're constantly "spinning" 24/7, consuming electricity and generating heat that needs to be cooled by expensive air conditioning equipment. Tape storage remains idle in a library slot or on a shelf when not in use, consuming no energy, which means far less CO2 is emitted into the atmosphere when compared to disk.
*According to a study by Brad Johns Consulting, comparing the average cost for disk and tape used for archiving over 10 years.
Tape storage also provides an opportunity for reducing the total cost of your data ownership. The energy savings alone contribute significantly to your bottom line, but tape itself is simply less expensive in total cost of ownership than other forms of storage. Check out our whitepaper from Brad Johns Consulting to find out how tape storage can drive an 86% reduction in costs compared to disk solutions.

An eco-friendly solution

Reduces carbon emissions and carbon footprint

Reduces costs per TB of storage as well as total cost of data ownership

More reliable and secure than disk solutions

Has a well-defined future migration road map

Effective defense against cyber crime
Check out our "Built on Tape" guide for more information about tape and its benefits.

Energy hungry server and HDD farms are forcing hyperscale data centers to move as much low-activity, archival and cold data to tape as possible to minimize energy consumption. As a result of these forces, tape has become a pressure relief valve for unabated hyperscale expansion".
- Fred Moore, President, Horison Information Strategies

As I mentioned last year, tape is not dead and is far from disappearing anytime soon. As a matter of fact, tape is very likely to become even more popular because of its cost profile and energy efficiency as a medium as well as its seemingly unlimited ability to store exponentially growing amounts of data".
- Christophe Bertrand, Senior Analyst, Enterprise Strategy Group

By identifying cold data and moving it to modern data tape storage, organizations can dramatically reduce energy consumption and associated carbon emissions while also lowering data center capital and operational expenses".
-Brad Johns, Brad Johns Consulting LLC

Some organizations use low-cost disk for archival purposes, and while it is less expensive than SSD and performance HDD technologies, it is inherently more expensive than tape and has a higher total cost of ownership associated with power and cooling".
- Phil Goodwin, Research Director, Multi-cloud Data Management for Protection, IDC
Tape storage involves storing digital data on magnetic tape as opposed to disk. The format dates back to the 1950s when a 12 inch reel of tape held just 2 MBs. Today, this tried-and-true data storage method can store up to 20 TB in a palm sized cartridge.
Yes, tape backup is still relevant! Tape provides an efficient, cost-effective method that organizations can use to quickly back up large amounts of data. It's also very secure — tape has fewer cybercrime vulnerabilities than either cloud or hard-disk storage.
Tape data storage is often used for cold data. That's data that you need to keep for various reasons, such as compliance or to maintain a complete archive of records, but that you don't need to access on a regular basis. It's estimated that 60% or more of stored data is cold data that can be archived onto less expensive, environmentally friendly options such as tape.
Tape's media life is much longer than disk. New tape media can be stored for 30 years or more, making it an ideal solution for long-term data archiving.
The future of data storage will depend on a mix of complementary storage devices. Data is growing at exponential rates across the globe, and the need to find sustainable ways to store data is also growing. A desire to cut down on carbon emissions and support cost savings certainly positions tape as a major player in the future of data storage.